Back To Top
By Jan Davies • Last Updated: 06-05-2024 SHOP NOW What is Metformin? Metformin is a medication commonly prescribed to manage blood sugar levels in people...

By Jan Davies • Last Updated: 06-05-2024
Metformin is a medication commonly prescribed to manage blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. It works by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. Metformin has been a cornerstone in diabetes treatment for years, proving its efficacy and relative safety for most patients.
Despite its benefits, Metformin can have side effects, particularly gastrointestinal ones. Understanding how the medication works and the potential side effects is crucial for anyone starting this treatment.
Metformin, a widely prescribed medication for controlling blood glucose levels, is known for its efficacy but also for its potential side effects, one of which includes gastrointestinal discomfort. A frequently asked question by many patients is: does metformin cause loose stools or diarrhea? Indeed, this is one of the more common side effects associated with the drug.
The reason for this discomfort is that Metformin can alter the ability of the intestines to absorb nutrients effectively, which may lead to an imbalance in the digestive process. Secondly, Metformin can affect the “good bacteria” that live in your intestines, which are important for helping you digest your food properly. These changes can sometimes manifest as diarrhea, which can range from mild to severe.
It’s crucial to recognize that while some individuals might encounter these symptoms, others may not experience any gastrointestinal issues at all. This variability is part of the complexity of how different bodies react to the same medication. For those who do suffer from diarrhea while taking Metformin, there are several strategies that can help manage this side effect, ensuring that the treatment’s benefits can still be enjoyed without undue discomfort. Additionally, for those interested in understanding the gastrointestinal side effects, here is a comprehensive study that has documented the effects of Metformin on diarrhea.

Navigating your diet while on Metformin can be challenging, especially when certain foods might trigger or worsen diarrhea. Here’s a curated list of common culprits that those taking Metformin might want to consume with caution:
By being mindful of these foods and monitoring how your body reacts, you can help reduce the risk of diarrhea and maintain greater comfort while managing your condition with Metformin. However, individual tolerances will vary, so it’s important to listen to your body and adjust your diet accordingly. If you’re experiencing persistent gastrointestinal side effects, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Additional information : “What is a healthy balanced diet for Diabetics – Diabetes UK”.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is another condition for which Metformin is often prescribed. Women with PCOS are generally advised to avoid high-glycemic index foods, as these can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Moreover, dairy products and caffeine can also worsen diarrhea in some individuals.
Sticking to a PCOS-friendly diet while on Metformin may help reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects and promote better overall health. In addition, for those seeking more information about polycystic ovary syndrome, we invite you to explore our informative blog post titled “What is PCOS?”.
Managing Metformin-induced diarrhea involves dietary adjustments, such as limiting foods that exacerbate the issue. Moreover, your doctor may recommend a gradual increase in your Metformin dose to help your body adjust. Over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications may also be beneficial, but always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
For some people, switching to the Metformin extended-release version can reduce gastrointestinal side effects, including diarrhea. Here at Meds for Less, you can securely and conveniently buy Metformin for your diabetes treatment needs and browse our extensive selection of diabetes management treatments.
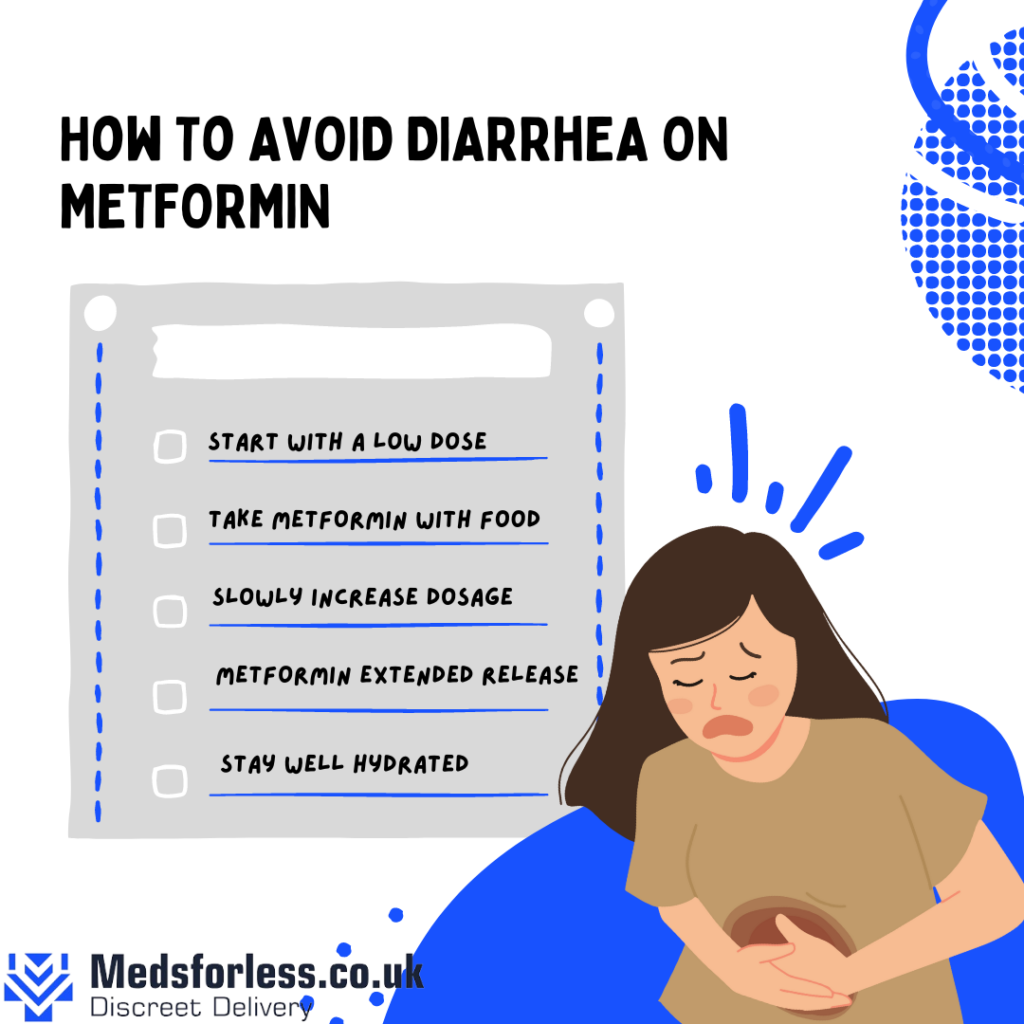
A well-balanced diet is essential when taking Metformin. Focus on whole foods like lean proteins, whole grains, and plenty of vegetables. These foods are not only nutritious but also tend to be gentler on the stomach. Additionally, staying hydrated and eating smaller, more frequent meals can help alleviate metformin stomach pain. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and kefir, can also support gut health and potentially reduce diarrhea symptoms.
Here’s a list of diabetes-friendly foods that complement Metformin treatment:
Firstly, metformin is known to influence the activity of the intestines, potentially altering gut motility. This means that it can speed up the passage of food through the digestive system, which does not allow for sufficient time for water to be absorbed, resulting in looser stools.
Moreover, metformin may have an effect on the gut’s microbiota—the complex community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. It can alter the composition and function of these microbial populations, which can influence digestive processes and contribute to symptoms like diarrhea.
Another aspect to consider is metformin and lactic acidosis , this increases the lactic acid levels in the intestine, leading to a condition known as lactic acidosis, which can affect bowel movements as well.
While most people tolerate metformin well, like any medication, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Here is a list of potential side effects associated with metformin:
Individual reactions to metformin can vary, and not everyone will experience these side effects. For more detailed information on metformin’s side effects and usage, you can refer to the Metformin patient information leaflet.
Weight loss can be a side effect of Metformin, although it’s not its primary use. The medication can lead to a decrease in appetite, which may contribute to weight loss in some individuals. However, it’s important to maintain a healthy diet and consult with your healthcare provider about any significant weight changes while on Metformin. Read our blog “Metformin for Weight Loss: Does it Work?” for more information.
Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal discomfort, which often improve over time.
While metformin is safe for many individuals, it may not be suitable for those with severe kidney problems, liver disease, or a history of lactic acidosis. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting metformin.
No FAQs available.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |